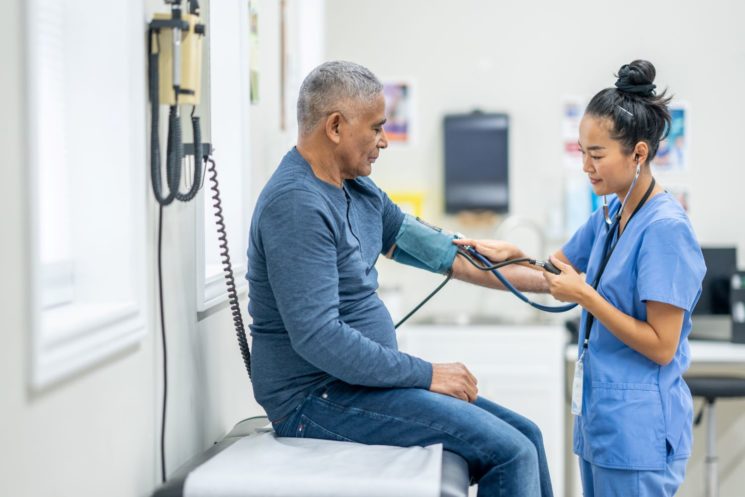
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 46% of adults with hypertension don't realise they have the condition. This is because hypertension doesn’t typically present with symptoms until it has reached a critical stage. 1 in 3 adults will develop hypertension during their life.
Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to serious health problems, including strokes, heart attacks, heart failure, kidney failure, visual impairment and more – which is why it’s important to have your blood pressure checked regularly. Find out more about hypertension and renal denervation, an advanced solution for treatment-resistant cases, in this blog.
What is hypertension?
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is when the force of your blood against the walls of your arteries (the tubes that carry blood around the body) is too high. It’s a common condition, especially in older adults, but it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated.
Throughout the day, your blood pressure naturally goes up and down – particularly if you’re active – and your arteries stretch to compensate for this. However, if your blood pressure is high when resting, this is a cause for concern.
When you have high blood pressure, your arteries can stiffen which makes it easier for fatty deposits to build up within them. This is what can eventually lead to serious complications, such as heart attacks and strokes.
How is hypertension diagnosed?
You can have your blood pressure checked at your GP practice or a dedicated hypertension clinic.
Blood pressure is measured using an electric monitor connected to an inflatable cuff, which is placed around the upper arm. You will receive two numbers:
- systolic pressure (the higher number) – the pressure against your arteries when your heart is pumping blood around your body
- diastolic pressure (the lower number) – the pressure in your arteries when your heart relaxes between beats
To diagnose hypertension, you will need your blood pressure measured more than once; this is because blood pressure fluctuates throughout the day. You may be provided with a blood pressure monitor to use at home, or a 24-hour monitor (called ambulatory blood pressure monitoring) that checks your blood pressure throughout the day. A clinician will look at your results to determine your average blood pressure.
Depending on your results, you may be advised to have further diagnostic tests, such as an ECG or echocardiogram, to rule out additional causes.
Stages of hypertension
There are several stages of hypertension:
- normal – where blood pressure is between 90/60mmHg and 120/80mmHg
- elevated or ‘prehypertension’ – where blood pressure levels are consistently between 120 and 129mmHg systolic and less than 80mmHg diastolic
- stage 1 – where blood pressure levels are consistently between 130 and 139mmHg systolic or 80 to 89 mmHg diastolic
- stage 2 – where blood pressure is consistently at or above 140/90mmHg
- stage 3 or ‘hypertension crisis’ – where blood pressure is consistently at or above 180/120mmHg
Treatment depends on the grading of your hypertension. Stage 1 hypertension can often be managed with lifestyle changes, while stage 2 will also require medication. Stage 3 requires immediate medical attention.
Renal denervation for hypertension
Renal denervation is an advanced interventional therapy recommended for patients who have treatment-resistant hypertension or who cannot tolerate medication due to side effects. It works by reducing the activity of nerves surrounding the renal arteries that contribute to high blood pressure.
The renal arteries supply blood to your kidneys; inside the wall of these arteries are nerves that help control blood pressure. When these nerves are overactive – as they often are in treatment-resistant hypertension patients – they can contribute to hypertension.
A small incision is created in the groin so that a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) can be inserted and guided into the renal arteries. Heat energy is then delivered through the catheter to neutralise the hyperactive nerves that contribute to hypertension. The procedure lasts around an hour, and most patients will be discharged the same day.
Benefits of renal denervation
As well as effectively lowering blood pressure long term, renal denervation patients can also benefit from:
- Reduced reliance on medication – Over time, some patients may find their reliance on medication is reduced, or that they don’t need as many medications as before.
- Enhanced existing medications – Some patients may find that their existing medications perform more effectively following renal denervation.
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease – Patients are less likely to develop serious conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
Renal denervation at Cromwell Hospital
At Cromwell Hospital, renal denervation is provided by Dr Sayan Sen and his specialist cardiac group One Heart Clinic.
Dr Sen is an internationally renowned cardiologist specialising in the assessment and management of patients with hypertension.
One Heart Clinic is a specialist group comprising of over 25 cardiologists who work collaboratively to deliver the best cardiac care for you and your heart.
To enquire about renal denervation, please contact Cromwell Hospital’s Self-Pay team on +44 (0)20 7244 4886.